Close
responsive-lightbox domain was triggered too early. This is usually an indicator for some code in the plugin or theme running too early. Translations should be loaded at the init action or later. Please see Debugging in WordPress for more information. (This message was added in version 6.7.0.) in /home/kiju52ce/public_html/development/wp-includes/functions.php on line 6114updraftplus domain was triggered too early. This is usually an indicator for some code in the plugin or theme running too early. Translations should be loaded at the init action or later. Please see Debugging in WordPress for more information. (This message was added in version 6.7.0.) in /home/kiju52ce/public_html/development/wp-includes/functions.php on line 6114
Approach Words: Smart City, Sustainability, Urban Livability
Public Policy Instruments: Financial Mechanism, Organization, Physical Intervention, Planning
Tarboul Industrial City is a large-scale industrial development project in Egypt, branded as the “Largest Investment Zone in The Middle East.”1 The project’s vision is to develop a green, smart, and livable industrial city as an “attractive destination for global investment and worldwide industries.” The project aligns with Egypt’s Vision 2030 and its goals of achieving high, inclusive, and sustainable economic growth in the country.2 i
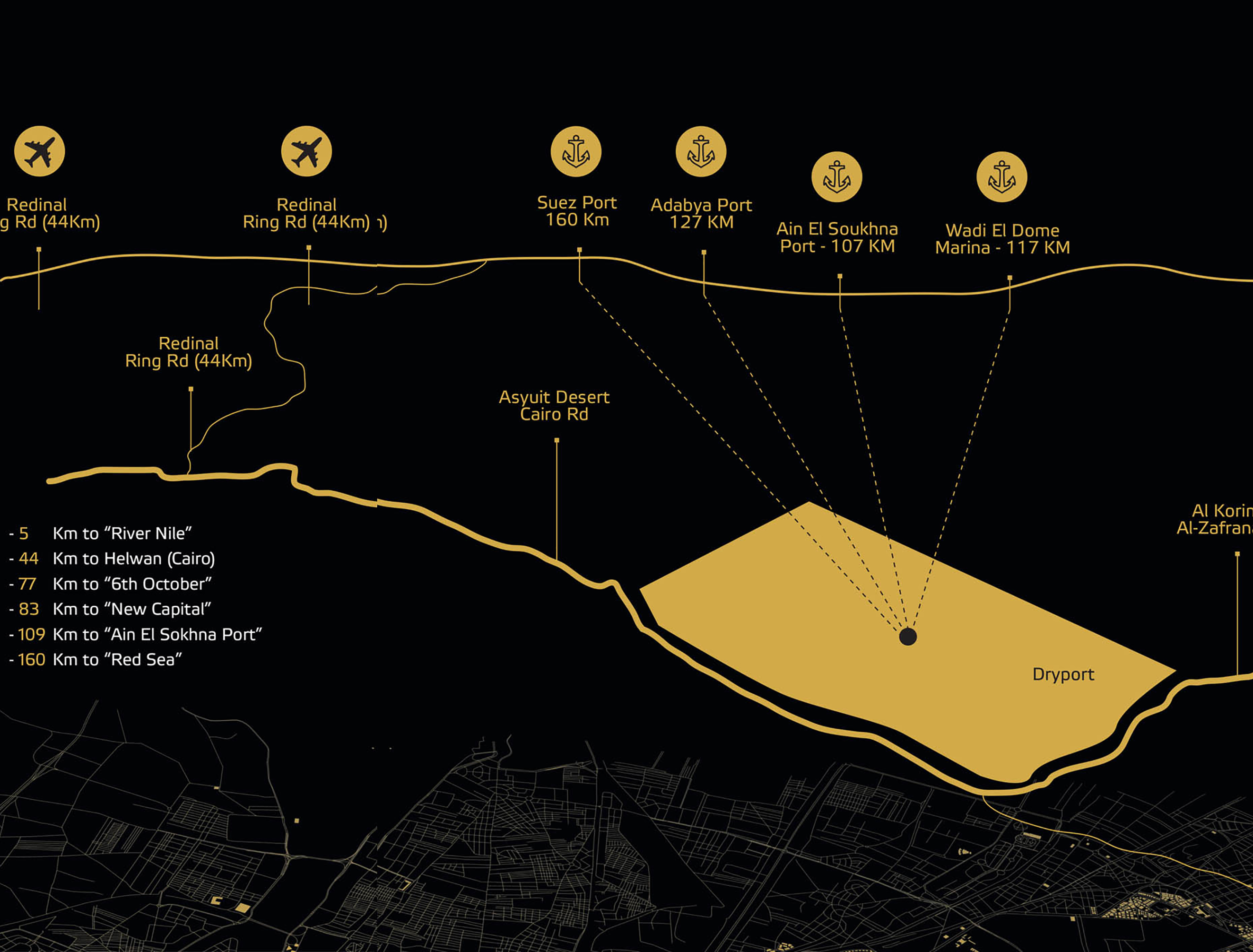
Title: Location of Tarboul Industrial City.
Source: Click Here
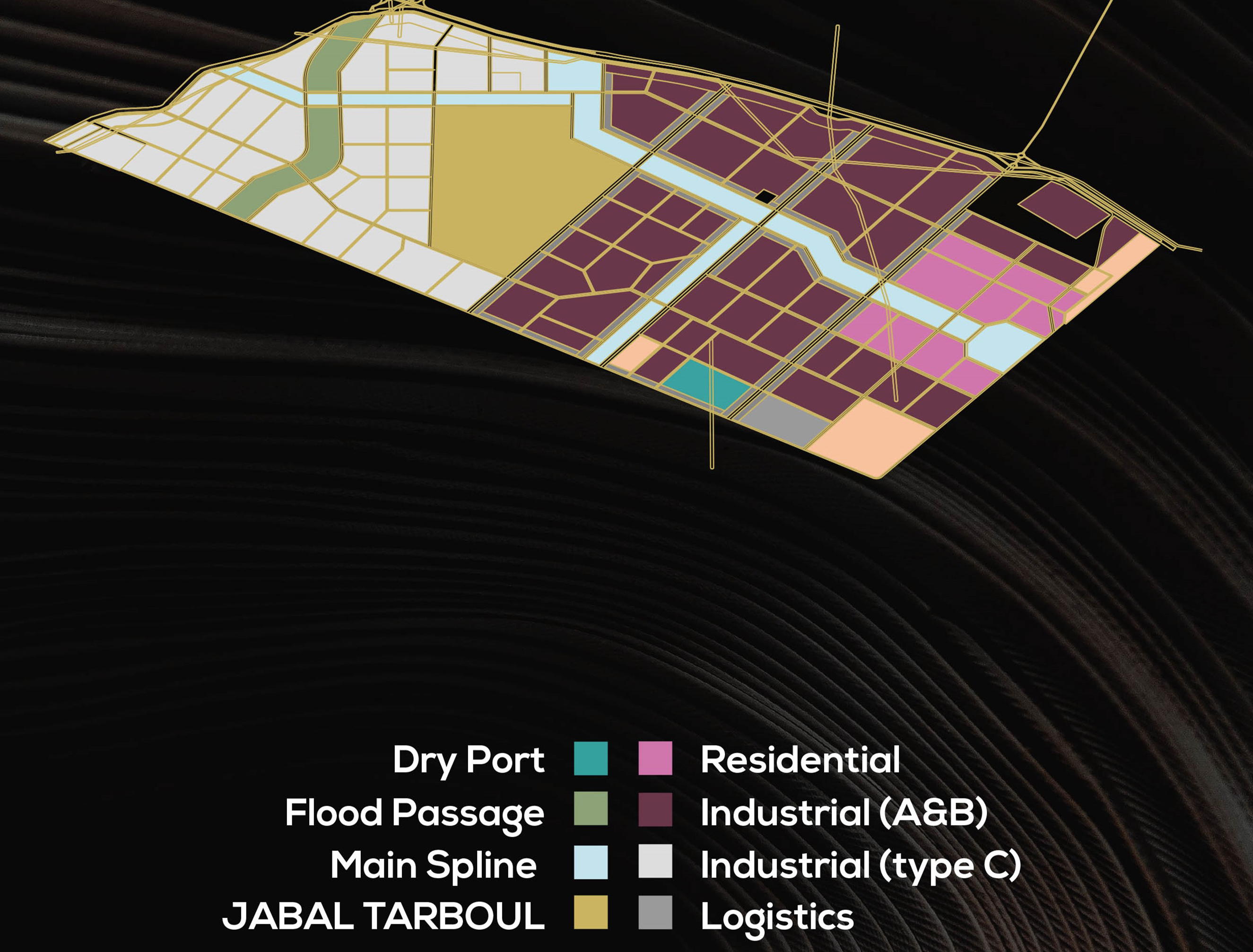
Title: Land Use Map of Tarboul Industrial City.
Source: Click Here

Title: Three-Dimensional View of the Project During Cairo ICT 2022.
Source: Click Here
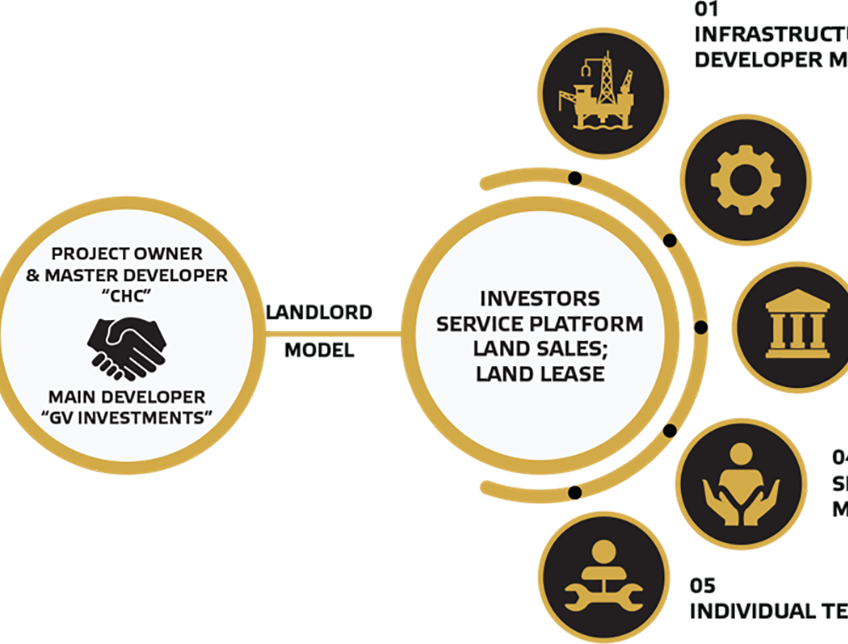
Title: Public-Private Partnership Model in Tarboul Industrial City.
Source: Click Here
To implement the project’s vision, a comprehensive master plan was proposed extending along a vast area of 109 square kilometers in southern Giza near the town of Atfih.3 The master plan features a multi-core industrial city combining various industrial services, logistics facilities, residential clusters, and training areas:4
Tarboul Industrial City declares to be committed to sustainable production.10 This includes green manufacturing, renewable energy supply covering around 20% of its energy needs,11 and recycled waste.12 In terms of infrastructure, the project claims to use smart infrastructure features, namely for drinking water and sewage gas facilities, and ICT network and services.13
In this project, the industrial activities are designed to enhance economic growth and diversify Egypt’s industrial base in Giza, which aims to stimulate development across various sectors, including manufacturing, logistics, commercial, and construction industries.14 The city aims to create more than 500,000 direct and indirect jobs.15

Owner/Developer

Consultant/Designer

Contractor/Implementer
The General Authority for Investment and Free Zones (GAFI) approved the project under the investment zones system in August 2023 on the site previously allocated for housing construction.16 While the General Authority for Construction and Housing Cooperatives (CHC), which is the landowner, was previously designated to carry out the Tarboul Project, the GV Real Estate Development Company is the master developer in charge of developing the plans and inviting private developers in collaboration with the CHC.17 This public-private approach aims to “increase private sector participation in the industrial sector and in the localization of technology.”18
The project is operated, in terms of permits and licenses, by the Tarboul Management Company, which includes “representatives of government agencies, such as the Industrial Development Authority, the Ministry of the Environment, the Giza Governorate, and the Civil Defense and the Investment Authority.”19 The project will be implemented in phases until 2035, with an estimated construction cost of over $3 billion.20
Project Link
Endnotes
References